DK Earth: Islands
An island is an area of land smaller than a continent and entirely surrounded by water. Islands range from single rocks to huge landmasses, such as the island of Greenland. There are two main types of island—continental islands and oceanic islands. Islands are also found in rivers and lakes.
Continental islands are found in shallow seas off large landmasses. They were formed when rising seas (for example, at the end of an ice age) cut off part of the land from a continent. Great Britain is an example of a continental island.
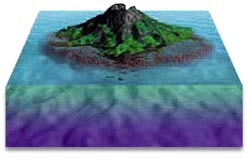
Volcanic islands are formed by volcanic activity on the seabed, often near the boundaries of the tectonic plates that form Earth’s crust. Where two plates pull apart, lava erupts to form an undersea ridge. Layers of lava build up until a ridge breaks the sea’s surface to form an island. Sometimes a whole chain of volcanic islands, called an island arc, is formed in this way. Some island arcs contain thousands of islands.
In November 1963, sailors saw a plume of smoke and ash rising from the sea off Iceland during an undersea volcanic eruption. A day later, as the eruption continued, lava broke the surface to form land. The new island was named Surtsey, after the Norse god of fire.
A coral reef is formed from the hard, shelly remains of coral polyps. These tiny creatures live in large colonies on rocks in shallow, sunlit water, such as the top of a seamount. When they die, their chalky, tube-shaped skeletons remain, and new, young coral grows on top. The coral skeletons build up over many years until they reach the sea’s surface, forming a reef.