DK Science: Motion
Everything in the world is moving. Even things that seem still are in motion, because the atoms inside them are vibrating. An object moves from one place to another when forces act on it and those forces are not balanced. When a force in one direction changes the SPEED or VELOCITY of an object, or the way it moves, this is known as ACCELERATION.
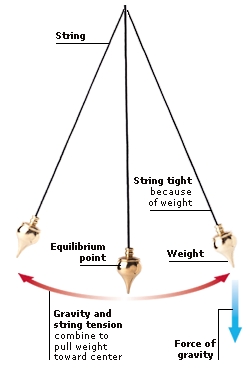
A clock’s pendulum moves back and forth because the forces that act on it are not balanced. The weight on the pendulum and the tightness of the string constantly try to pull the pendulum towards the centre. But its weight and speed swing it past the point of balance (equilibrium point). So the velocity of the pendulum is constantly changing.
A roller coaster’s carriages accelerate (gather speed) when the force of gravity pulls them down a steep incline. The speed and weight of the carriages then keeps them moving, even when they continue in a straight line or climb upwards.
When we think of speed, we think of cars, jet planes, anything that moves quickly. To scientists, however, speed means things moving fast or slow. Speed is defined as the distance an object travels in a certain amount of time. Fast cars travel at higher speed than slow cars, so they can go further in the same time.
Velocity is the speed of an object moving in a particular direction. Two cars driving at the same speed have different velocities if one of them goes north and the other goes south. Velocity is measured in metres per second (mps), which divides the distance travelled by the time taken, in a specific direction.

When moving objects change speed, they change velocity. As they change direction, they also change velocity, even if their speed stays the same. When the bike goes faster or slower, the force that makes it change velocity is the engine or brakes. When it turns, the rider provides the force by turning the handlebars.
When we talk of things accelerating, we usually mean they are speeding up. In science, however, acceleration means any change in an object’s velocity, whether it goes faster, slower, or changes direction. According to Newton’s second law of motion, a force is always needed to produce an acceleration. The bigger the force, the faster the change in velocity.

An object that moves in a circle, such as this ball swinging on a string, constantly changes direction. Even when it turns at a steady speed, its velocity is always changing. It takes a force to make it accelerate like this. When an object moves in a circle, the force that constantly pulls it towards the centre and stops it flying off in a straight line is called centripetal force.
