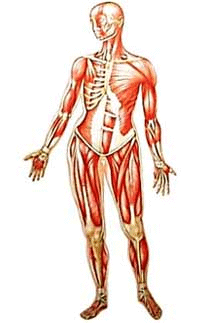
DK Human Body: Muscle
Body movement is brought about by muscle, a tissue that can contract. There are three main types: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Most muscle is made of elongated cells called MUSCLE FIBERS.
Smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are involuntary—they work automatically, without our conscious control. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of the intestines, stomach, esophagus, and other organs. It contracts slowly and rhythmically to push food through the digestive system. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and works continuously without tiring.
Skeletal muscles move bones by pulling on them. Because we control this movement, they are called voluntary muscles. Muscles can pull but not push, so skeletal muscles are often arranged in pairs that pull bones in opposite directions.
Individual muscle cells are called muscle fibers. Skeletal muscle is made up of thousands of muscle fibers arranged in parallel bundles. Each fiber is thinner than a hair and can measure up to 12 in (30 cm) long.
A muscle fiber is made up of myofibrils, which are made of thinner strands called myofilaments. When myofilaments are stimulated by a nerve impulse, they slide over each other, shortening the muscle. The more signals there are, the more the muscle contracts, until it shortens to as little as 70 percent of its relaxed length.
The three main types of muscle fiber work in very different ways. Smooth muscle can contract for prolonged periods. Skeletal muscle contracts quickly and powerfully, but only for short periods of time. Cardiac muscle contracts rhythmically and continually without tiring.
Smooth muscle has spindle-shaped fibers that overlap. It contracts about 50 times more slowly than skeletal muscle.
Skeletal muscle contains very long, slender muscle fibers arranged in parallel, which give it a striped appearance.